Why experts recommend ditching racial labels in genetic studies
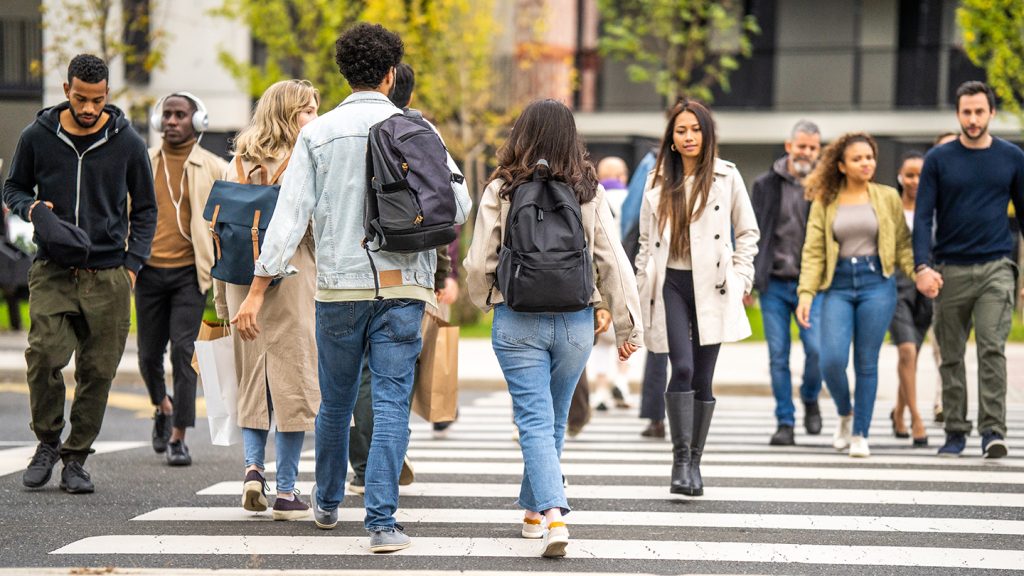

Race should no longer be used to describe populations in most genetics studies, a panel of experts says.
Using race and ethnicity to describe study participants gives the mistaken impression that humans can be divided into distinct groups. Such labels have been used to stigmatize groups of people, but do not explain biological and genetic diversity, the panel convened by the U.S. National Academies of Sciences, Engineering and Medicine said in a report on March 14.
In particular, the term Caucasian should no longer be used, the committee recommends. The term, coined in the 18th century by German scientist Johann Friedrich Blumenbach to describe what he determined was the most beautiful skull in his collection, carries the false notion of white superiority, the panel says.
Worse, the moniker “has also acquired today the connotation of being an objective scientific term, and that’s what really led the committee to take objection with it,” says Ann Morning, a sociologist at New York University and a member of the committee that wrote the report. “It tends to reinforce this erroneous belief that racial categories are somehow objective and natural characterizations of human biological difference. We felt that it was a term that … should go into the dustbin of history.”
Similarly, the term “black race” shouldn’t be used because it implies that Black people are a distinct group, or race, that can be objectively defined, the panel says.
Racial definitions are problematic “because not only are they stigmatizing, they are historically wrong,” says Ambroise Wonkam, a medical geneticist at Johns Hopkins University and president of the African Society of Human Genetics. Race is often used as a proxy for genetic diversity. But “race cannot be used to capture diversity at all. Race doesn’t exist. There is only one race, the human race,” says Wonkam, who was not involved with the National Academies’ panel.
Race might be used in some studies to determine how genetic and social factors contribute to health disparities (SN: 4/5/22), but beyond that race has no real value in genetic research, Wonkam adds.
Researchers could use other identifiers, including geographical ancestry, to define groups of people in the study, Wonkam says. But those definitions need to be precise.
For instance, some researchers group Africans by language groups. But a Bantu-speaking person from Tanzania or Nigeria where malaria is endemic would have a much higher genetic risk of sickle cell disease than a Bantu-speaking person whose ancestors are from South Africa, where malaria has not existed for at least 1,000 years. (Changes in genes that make hemoglobin can protect against malaria (SN: 5/2/11), but cause life-threatening sickle cell disease.)
Genetic studies also have to account for movements of people and mixture between multiple groups, Wonkam says. And labeling must be consistent for all groups in the study, he says. Current studies sometimes compare continent-wide racial groups, such as Asian, with national groups, such as French or Finnish, and ethnic groups, such as Hispanic.
An argument for keeping race in rare cases
Removing race as a descriptor may be helpful for some groups, such as people of African descent, says Joseph Yracheta, a health disparities researcher and the executive director of the Native BioData Consortium, headquartered on the Cheyenne River Sioux reservation in South Dakota. “I understand why they want to get rid of race science for themselves, because in their case it’s been used to deny them services,” he says.
But Native Americans’ story is different, says Yracheta, who was not part of the panel. Native Americans’ unique evolutionary history have made them a valuable resource for genetics research. A small starting population and many thousands of years of isolation from humans outside the Americas have given Native Americans and Indigenous people in Polynesia and Australia some genetic features that may make it easier for researchers to find variants that contribute to health or disease, he says. “We’re the Rosetta stone for the rest of the planet.”
Native Americans “need to be protected, because not only are our numbers small, but we keep having things taken away from us since 1492. We don’t want this to be another casualty of colonialism.” Removing the label of Indigenous or Native American may erode tribal sovereignty and control over genetic data, he says.
The panel does recommend that genetic researchers should clearly state why they used a particular descriptor and should involve study populations in making decisions about which labels to use.
That community input is essential, Yracheta says. The recommendations have no legal or regulatory weight. So he worries that this lack of teeth may allow researchers to ignore the wishes of study participants without fear of penalty.
Still seeking diversity in research participants
Genetics research has suffered from a lack of diversity of participants (SN: 3/4/21). To counteract the disparities, U.S. government regulations require researchers funded by the National Institutes of Health to collect data on the race and ethnicity of study participants. But because those racial categories are too broad and don’t consider the social and environmental conditions that may affect health, the labels are not helpful in most genetic analyses, the panel concluded.
Removing racial labels won’t hamper diversity efforts, as researchers will still seek out people from different backgrounds to participate in studies, says Brendan Lee, who is president of the American Society of Human Genetics. But taking race out of the equation should encourage researchers to think more carefully about the type of data they are collecting and how it might be used to support or refute racism, says Lee, a medical geneticist at Baylor College of Medicine in Houston, who was not part of the panel.
The report offers decision-making tools for determining what descriptors are appropriate for particular types of studies. But “while it is a framework, it is not a recipe where in every study we do A, B and C,” Lee says.
Researchers probably won’t instantly adopt the new practices, Lee says. “It is a process that will take time. I don’t think it is something we can expect in one week or one evening that we’ll all change over to this, but it is a very important first step.”